SimplyAnalytics contains a myriad of geographic units. Descriptions of each are below.
Standard Geographies
States - are the primary governmental divisions of the United States. In addition to the 50 states, the Census Bureau treats the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands as the statistical equivalents of states for the purpose of data presentation.
Counties - Counties are the primary legal divisions of most states. Most counties are functioning governmental units, whose powers and functions vary from state to state.
Cities - Cities are referred to as Places by the Census. Places consist of "Incorporated Places" and "Census Designated Places (CDPs). An incorporated place is established to provide governmental functions for a concentration of people as opposed to a minor civil division, which generally is created to provide services or administer an area without regard, necessarily, to population. Places always are within a single state or equivalent entity, but may extend across county and county subdivision boundaries. An incorporated place usually is a city, town, village, or borough, but can have other legal descriptions. CDPs are the statistical counterparts of incorporated places, and are delineated to provide data for settled concentrations of population that are identifiable by name but are not legally incorporated under the laws of the state in which they are located.
ZIP Codes (ZCTAs) - are approximate area representations of U.S. Postal Service (USPS) five-digit ZIP Code service areas that the Census Bureau creates using whole blocks to present statistical data from censuses and surveys. The Census Bureau defines ZCTAs by allocating each block that contains addresses to a single ZCTA, usually to the ZCTA that reflects the most frequently occurring ZIP Code for the addresses within that tabulation block.
Census Tracts - are small, relatively permanent statistical subdivisions of a county or equivalent entity that are updated by local participants prior to each decennial census as part of the Census Bureau's Participant Statistical Areas Program. Census tracts generally have a population size between 1,200 and 8,000 people, with an optimum size of 4,000 people. A census tract usually covers a contiguous area; however, the spatial size of census tracts varies widely depending on the density of settlement. Census tract boundaries are delineated with the intention of being maintained over a long time so that statistical comparisons can be made from census to census.
Census Block Groups - are statistical divisions of census tracts, generally defined to contain between 600 and 3,000 people, and are used to present data and control block numbering. A block group consists of clusters of blocks within the same census tract that have the same first digit of their four-digit census block number.
Nielsen DMA (exclusive to those institutions subscribing to the Scarborough dataset) - A DMA region is a group of counties that form an exclusive geographic area in which the home market television stations hold a dominance of total hours viewed. There are 210 DMA regions, covering the entire continental United States, Hawaii, and parts of Alaska. The DMA boundaries and DMA data are owned solely and exclusively by Nielsen.
Optional Geographies - Please click on Project Settings to Activate These
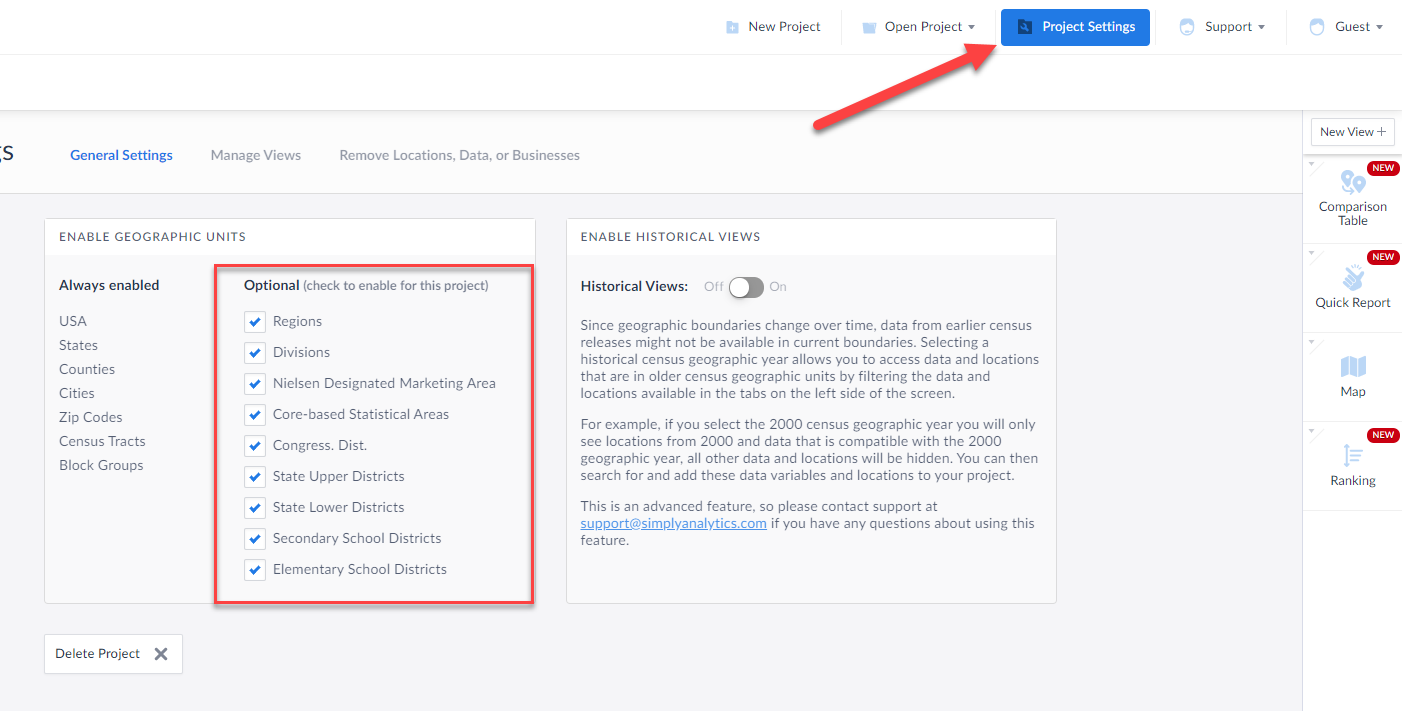
Regions - are groupings of states and the District of Columbia that subdivide the United States for the presentation of census data. There are four census regions—Northeast, Midwest, South, and West. Each of the four census regions is divided into two or more census divisions. Each census region is identified by a single-digit census code.
Divisions - are groupings of states and the District of Columbia that are subdivisions of the four census regions. There are nine census divisions, and each is identified by a single-digit census code. Puerto Rico and the Island Areas are not part of any census region or census division.
Core-Based Statistical Areas - consist of the county or counties or equivalent entities associated with at least one core (urbanized area or urban cluster) of at least 10,000 population, plus adjacent counties having a high degree of social and economic integration with the core as measured through commuting ties with the counties associated with the core. The general concept of a CBSA is that of a core area containing a substantial population nucleus, together with adjacent communities having a high degree of economic and social integration with that core. The term "core based statistical area" became effective in 2003 and refers collectively to metropolitan statistical areas and micropolitan statistical areas.
Congressional Districts - are the 435 areas from which people are elected to the U.S. House of Representatives. After the apportionment of congressional seats among the states based on decennial census population counts, each state with multiple seats is responsible for establishing congressional districts for the purpose of electing representatives. Each congressional district is to be as equal in population to all other congressional districts in a state as practicable.
State Upper Districts - are the areas from which members are elected to state legislatures. The upper district refers to the Senate.
State Lower Districts - are the areas from which members are elected to state legislatures. The lower district refers to the House.
Secondary School Districts - are geographic entities within which state, county, local officials, the Bureau of Indian Affairs, or the U.S. Department of Defense provide public educational services for the area’s residents. The Census Bureau obtains the boundaries, names, local education agency codes, and school district levels for school districts from state and local school officials. The secondary school districts provide education to the upper grade/age levels. Unified school districts provide education to children of all school ages in their service areas. In general, where there is a unified school district, no elementary or secondary school district exists; and where there is an elementary school district, the secondary school district may or may not exist.
Elementary School Districts - are geographic entities within which state, county, local officials, the Bureau of Indian Affairs, or the U.S. Department of Defense provide public educational services for the area’s residents. The Census Bureau obtains the boundaries, names, local education agency codes, and school district levels for school districts from state and local school officials. The elementary school districts provide education to the lower grade/age levels. Unified school districts provide education to children of all school ages in their service areas. In general, where there is a unified school district, no elementary or secondary school district exists; and where there is an elementary school district, the secondary school district may or may not exist.
Sources:
https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/geography/about/glossary.html
https://www.nielsen.com/us/en/intl-campaigns/dma-maps/